
A baseball pitched by a fast Major League pitcher has a kinetic energy of approximately 230 J. One calorie (1 1/1000 of a kilocarie of food consumed or metabolic energy expended) equals 4.186 J. The amount of energy one utilizes in lifting a cup of water from the table to one's mouth equals approximately 1 Joule. One kilogram (kg) of mass is equivalent to exactly 89,875,517,873,681,764 joules (according to E= mc 2 with m = 1 kg and speed of light c = 299,792,458 m/s). Those include: erg foot pound watt second watt hour kilowatt hour thermochemical calorie International Table calorie kilocalorie thermochemical Btu therm quad cubic meter natural gas ton of oil equivalent ton of coal equivalent ton of TNT electron volt hartree inverse meter inverse second kelvin kilogram. Whereas the joule is the standard SI unit of energy, many other units of energy, all convertible to joules, are used in particular circumstances. Other units of energy convertible to joules Often, kilojoules (kJ) are used, kJ = 10 3 J. One joule represents a relatively small amount of energy it takes roughly 100,000 J (10 5 J) to heat a cup of water from room temperature to its boiling point under standard conditions. The joule is named for James Prescott Joule (1818 - 1889), who studied the relation between mechanical and heat energy discovered earlier by count Rumford. One calorie of heat is the equivalent of 4.186 J. The joule is also used to measure thermal energy. The amount of energy delivered by a one watt source of power in one second is one Joule. One joule measures the energy released by a electric charge of one coulomb dropping one volt in absolute value of electrical potential. One may also use electric units to define the joule. 'Joule' is variously pronounced 'jool' (rhymes with 'jewel') or 'joul' (rhymes with 'jowl'). It follows that J (joule) is expressed in SI basic units as: The mechanical quantities involved have the SI units: One newton equals a force that produces an acceleration of one meter per second (s) per second on a one kilogram (kg) mass. One joule equals the work done (or energy expended) by a force of one newton (N) acting over a distance of one meter (m). 
You activate the rocket, and immediately deactivate it when the box reaches the end of the race.The joule (symbol J) is the SI unit of energy-a measure of the capacity to do work or generate heat. You hook up a rocket to this box that applies a constant force of 1 newton when active.

I you want a more visual example, imagine a box sitting at the starting line of a race that is exactly one meter long (maybe it's a race for snails, just bare with me here). In other words, 1 joule would be applying one newton to an object as that object moves across one meter of space. One Joule is equal to 1 kg(m 2)/(s 2), or one kilogram meter squared per second squared (e.i. you can visualize a Newton as a force that can be applied with your own hands when you push a box, throw a ball, or do anything else. For example, if you apply a force of 30 newtons to a 5-kg block for 10 seconds, at the end that object would be moving at 60 meters per second.
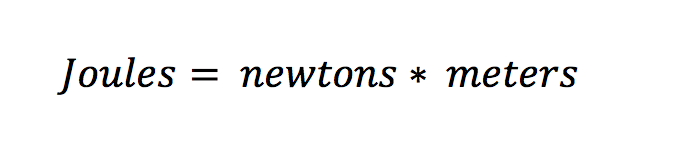
in other words, one newton of force is the force that is required to accelerate a 1-kg object by one meter per second every second that that force is applied.

One Newton is equal to one kg*m/(s 2), or one kilogram meter per second squared. The Joule and the Newton, like all units, can be defined in terms of mass, distance, and time.




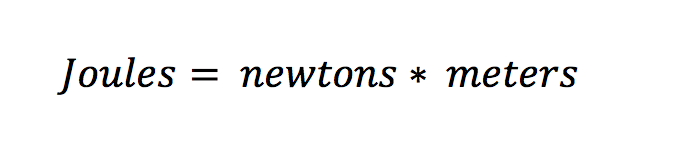



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
